 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Good practice ; Khon Kaen ESI (KESI) triage | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Relate topic ; Triage Training program | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KESI คืออะไร | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KESI เป็นการคัดแยกผู้ป่วย
กระทำโดยพยาบาลวิชาชีพที่มีประสบการณ์และผ่านการอบรมแล้ว เป็นการคัดแยกเน้นภาวะคุกคามต่อชีวิต
และการใช้ทรัพยากรเพื่อวินิจฉัยและรักษา ไม่ใช่การคัดแยกตามการวินิจฉัยโรค โดยหลักการแล้ว
สามารถยอมรับความผิดพลาดของการคัดแยกได้ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time guaruntee with KESI | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KESI 1
resuscitation สีแดง ต้องให้การช่วยเหลือทันที KESI 2 emergent สีชมพู ต้องได้รับการตรวจรักษาในเวลา 5-10 นาที KESI 3 urgent สีเหลือง รับการตรวจรักษาในเวลา 15-30 นาที KESI 4 Less-urgent สีเขียว สามารถรอรับการตรวจรักษาในเวลา 30-60 นาที KESI 5 non-urgent สีขาว สามารถรอรับการตรวจรักษาในเวลา 1-2 ชั่วโมง | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
คำถามในการคัดกรองตามระบบ
KESI | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
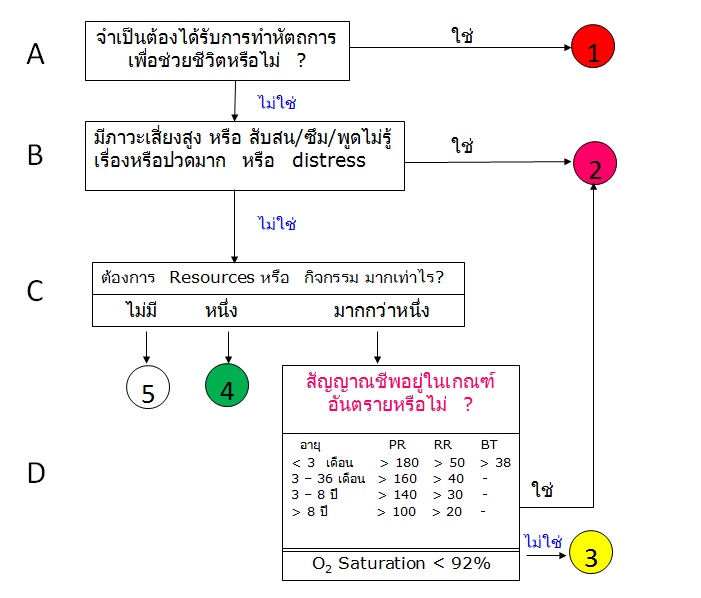
Decision Point A : ผู้ป่วยกำลังจะเสียชีวิตหรือไม่ ? ต้องได้รับการช่วยเหลือด้านทางเดินหายใจ
การให้ยา และการดูแลระบบไหลเวียนโลหิตอย่างรวดเร็วหรือไม่ ( Immediate Life-saving intervention) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immediate life-saving intervention ประกอบด้วย | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Decision Point B : ผู้ป่วยไม่ควรจะต้องรอใช่หรือไม่ ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ข้อสังเกต : การคัดกรองระบบนี้ต้องอาศัยความรู้และประสบการณ์ของพยาบาลเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ แต่ไม่ใช่ทั้งหมด และการคัดกรองมักไม่ต้องใช้สัญญาณชีพในการจัดกลุ่ม high risk เพียงแค่่อาจใช้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งในการพิจารณา Is this a high-risk situation ? ขึ้นกับการซักประวัติคร่าวๆ, การสังเกตเบื้องต้น และประสบการณ์ (sixth sense !!) Is the patient confused, lethargic or disoriented ? Is the patient in severe pain or distress ? พิจารณา เป็นระดับ 2 เมื่อมี | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ตัวอย่างของ High-risk
situations :
ตัวอย่างของ confused, lethargic
or disoriented
ตัวอย่างของ Severe Pain /
Distress
Distressed facial
expression, grimacing, crying Diaphoresis
Body posture Changes in vital signs – hypertension (HTN), tachycardia, and increased respiratory rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Decision Point C : Resource Needs ต้องใช้ทรัพยากรมากน้อยเพียงไร ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Resources หรือ กิจกรรม ของ KESI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Decision Point D :
the patient vital sign ? พิจารณาว่าสัญญาณชีพอยู่ในเกณฑ์อันตรายหรือไม่
? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pediatric consideration of
body temperature Neonate หรือทารกอายุ <3
เดือน มีไข้มากกว่า 38.0 C พิจารณาเป็น ระดับ
2
เด็กที่อายุมากกว่า 3 เดือน มีไข้มากกว่า 39.0 C ที่ไม่มีสาเหตุชัดเจนหรือได้รับวัคซีนไม่ครบ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
สรุป
การนำ KESI มาใช้ที่ห้องฉุกเฉิน
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
KESI เป็นการคัดแยกเน้นภาวะคุกคามต่อชีวิต
และการใช้ทรัพยากรเพื่อวินิจฉัยและรักษา ไม่ใช่การคัดแยกตามการวินิจฉัยโรค
สามารถยอมรับความผิดพลาดของการคัดแยกได้ ก้าวต่อไป ... สามารถนำมาใช้เพื่อคัดกรองสำหรับผู้มารับบริการเป็นผู้ป่วยนอก ทั้ง ER และ OPD ด้วย Protocol ที่เหมือนกัน | ||||||||||||||||||||||
แผนกอุบัติเหตุ-ฉุกเฉิน โรงพยาบาลขอนแก่น ชั้น 1 อาคารสิรินธร เลขที่ 54-56 ถ.ศรีจันทร์ ต.ในเมือง อ.เมือง จ.ขอนแก่น 40000
| ||||||||||||||||||||||